Sodium Borohydride CAS 16940-66-2 BH4Na
Sodium Borohydride CAS 16940-66-2 BH4Na, hot in Canada/USA/Europe, stock available.
BH4Na Basic Parameter
| Product Name: | Sodium Borohydride |
| Synonyms: | boron sodium hydride; sodium boranoate; NaBH4; Kodalk; Sodium tetrahydroborate; Sodium dioxoborate; sodium tetraborohydride; sodium tetrahydridoborate; Sodiooxyboron oxide; Sodium borohydride |
| CAS NO: | 16940-66-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | H4BNa |
| Molecular Weight: | 37.833 |
| Boiling Point: | 500ºC |
| Melting Point: | 400ºC (dec.) |
| Flash Point: | 69ºC |
| Density: | 1.07 |
| Water Solubility: | 550 g/L (25 ºC) |
CAS 16940-66-2 Picture

What is Sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4 (sometimes written as Na[BH4]). It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953.
Structure
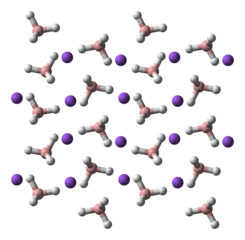
NaBH4 is a salt, consisting of the tetrahedral [BH4]− anion. The solid is known to exist as three polymorphs: α, β and γ. The stable phase at room temperature and pressure is α–NaBH4, which is cubic and adopts an NaCl-type structure, in the Fm3m space group. At a pressure of 6.3 GPa, the structure changes to the tetragonal β–NaBH4 (space group P421c) and at 8.9 GPa, the orthorhombic γ–NaBH4 (space group Pnma) becomes the most stable.
-
-
α-NaBH4 β-NaBH4 γ-NaBH4
-
Synthesis and handling
For commercial NaBH4 production, the Brown-Schlesinger process and the Bayer process are the most popular methods. In the Brown-Schlesinger process sodium borohydride is industrially prepared from sodium hydride (produced by reacting Na and H2) and trimethyl borate at 250–270 °C:
- B(OCH3)3 + 4 NaH → NaBH4 + 3 NaOCH3
Millions of kilograms are produced annually, far exceeding the production levels of any other hydride reducing agent. In the Bayer process, it is produced from inorganic borates, including borosilicate glass and borax (Na2B4O7):
- Na2B4O7 + 16 Na + 8 H2 + 7 SiO2 → 4 NaBH4 + 7 Na2SiO3
Magnesium is a less expensive reductant, and could in principle be used instead:
- 8 MgH2 + Na2B4O7 + Na2CO3 → 4 NaBH4 + 8 MgO + CO2
and
- 2 MgH2 + NaBO2 → NaBH4 + 2 MgO
Contact Anisa:
WhatsApp/Signal: +86 17671756304
Telegram: @rchemanisa
Element: @rchemanisa:matrix.org
Website:https://bmf-49851-31-2.com
Session: 05468ee84b6ca5c619560e29a92e664c358c08b4ea5c6c2d5d88f39e8c87dcb407









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.